10-Q: Quarterly report [Sections 13 or 15(d)]
Published on February 12, 2026
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM
(Mark One)
QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number 001-39267
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(IRS Employer Identification No.) |
(Address of principal executive offices & zip code)
(
(Registrant’s telephone number including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
|
Trading Symbol(s) |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
|
|
|
☒ |
Smaller reporting company |
||
|
|
|
|
Emerging growth company |
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ or No
We had
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
INDEX TO FORM 10-Q
3 |
|||
|
|
||
5 |
|||
|
|
|
|
ITEM 1. |
5 |
||
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2025 (Unaudited) and June 30, 2025 |
5 |
|
|
6 |
||
|
7 |
||
|
8 |
||
|
9 |
||
ITEM 2. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
23 |
|
ITEM 3. |
35 |
||
ITEM 4. |
35 |
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
ITEM 1. |
37 |
||
ITEM 1A. |
37 |
||
ITEM 2. |
37 |
||
ITEM 3. |
37 |
||
ITEM 4. |
37 |
||
ITEM 5. |
37 |
||
ITEM 6. |
38 |
||
|
|
||
39 |
|||
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Report contains forward-looking statements that are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control. Our forward-looking statements relate to future events or our future performance and include, but are not limited to, statements concerning our business strategy, future commercial revenues, market growth, capital requirements, new product introductions, expansion plans and the adequacy of our funding. All statements, other than statements of historical fact included in this Report, are forward-looking statements. When used in this Report, the words “could,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “estimate,” “expect,” “may,” “continue,” “predict,” “potential,” “project,” or the negative of these terms, and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain such identifying words. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements to be materially different from the information expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements.
Some of the risks and uncertainties that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by forward-looking statements include the following:
3
as well as other risks detailed under the caption “Risk Factors” in this Report and in other reports filed with the SEC. Although we believe that we have a reasonable basis for each forward-looking statement contained in this Report, we caution you that these statements are based on a combination of facts and important factors currently known by us and our expectations of the future, about which we cannot be certain. Such statements are based on assumptions and the actual outcome will be affected by known and unknown risks, trends, uncertainties and factors that are beyond our control or ability to predict. We have based the forward-looking statements included in this Report on information available to us on the date of this Report or on the date thereof. Except as required by law we undertake no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. You are advised to consult any additional disclosures that we may make directly to you or through reports that we, in the future, may file with the SEC, including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K.
All forward-looking statements included herein or in documents incorporated herein by reference are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained or referred to elsewhere in this Report.
4
PART I—FINANCIAL INFORMATION
ITEM 1. Financial Statements
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except par value and share amounts)
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
|
|
(Unaudited) |
|
|
|
|
||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Trade and other receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deposits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Trade and other payables |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued employee benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease liabilities, current portion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease liabilities, less current portion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Preferred stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Common stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
5
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(Unaudited)
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||||
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Total revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Research and development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
General and administrative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Loss from operations |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Other income (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Foreign currency transaction gain (loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Interest income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Gain on extinguishment of liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total other income, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Net loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Other comprehensive income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Unrealized foreign currency translation gain (loss) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Total comprehensive loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Net loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Net loss per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Basic and diluted |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Weighted average number of shares outstanding: basic and diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
6
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(Unaudited)
(in thousands, except share amounts)
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Loss |
|
|
Equity |
|
||||||
Balance at June 30, 2024 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
Exercise of pre-funded warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercise of Series 2 warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercise of common warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign currency translation loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance at September 30, 2024 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
Exercise of pre-funded warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercise of Series 2 warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercise of common warrants, net of issuance costs of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign currency translation gain |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Loss |
|
|
Equity |
|
||||||
Balance at June 30, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign currency translation gain |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance at September 30, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
Issuance of common stock sold for cash, net of offering costs of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||||
Exercise of pre-funded warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercise of Series 2 warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign currency translation loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Balance at December 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
7
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Unaudited)
(in thousands)
|
|
For the Six Months Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Amortization of right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain on extinguishment of liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Share-based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Trade and other receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid and other assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Trade and other payables |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accrued employee benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lease liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Purchase of property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Proceeds from the issuance of common stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Proceeds from exercise of pre-funded warrants, Series 2 warrants and common warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Share issuance transaction costs |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Effects of exchange rate changes on cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, end of period |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Supplemental cash flow information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Re-measurement of operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Exercise of warrants to shares of common stock |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
8
BENITEC BIOPHARMA INC.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
1. Business
Benitec Biopharma Inc. (the “Company”, “we”, “our”) is a corporation formed under the laws of Delaware, United States of America, on
The Company’s fiscal year end is June 30. References to a particular “fiscal year” are to our fiscal year end June 30 of that calendar year.
The consolidated financial statements of Benitec Biopharma Inc. are presented in United States dollars and consist of Benitec Biopharma Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries as listed below. Aside from Benitec Biopharma Proprietary Limited, the international subsidiaries are dormant.
|
|
Principal place of business/country of incorporation |
Benitec Biopharma Proprietary Limited (“BBL”) |
|
|
Benitec Australia Proprietary Limited |
|
|
Benitec Limited |
|
|
Benitec, Inc. |
|
|
Benitec LLC |
|
|
RNAi Therapeutics, Inc. |
|
|
Tacere Therapeutics, Inc. |
|
|
Benitec IP Holdings, Inc. |
|
2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The Company’s consolidated financial statements contained in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. (“GAAP”) for interim financial information and with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Article 8 of U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Regulation S-X. Accordingly, certain information and disclosures required by GAAP for annual financial statements have been omitted. In the opinion of management, all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, considered necessary for a fair presentation have been included. Interim financial results are not necessarily indicative of results anticipated for the full year. These consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s audited financial statements and accompanying notes included in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2025.
Reference is frequently made herein to the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”). This is the source of authoritative GAAP recognized by the FASB to be applied to non-governmental entities.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the Company’s accounts and the accounts of its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated.
9
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that impact the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in the Company’s consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. The most significant estimates and assumptions in the Company’s consolidated financial statements relate to accrued research and development expense and valuation of equity-based instruments issued for other than cash. These estimates and assumptions are based on current facts, historical experience and various other factors believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities and the recording of expenses that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ materially and adversely from these estimates. To the extent there are material differences between the estimates and actual results, the Company’s future results of operations will be affected.
Risks and Uncertainties
The Company is subject to risks and uncertainties common to early-stage companies in the biotechnology industry, including, but not limited to, development by competitors of new technological innovations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on key personnel, reliance on single-source vendors and collaborators, availability of raw materials, patentability of the Company’s products and processes and clinical efficacy and safety of the Company’s products under development, compliance with government regulations and the need to obtain additional financing to fund operations.
There can be no assurance that the Company’s research and development will be successfully completed, that adequate protection for the Company’s intellectual property will be obtained or maintained, that any products developed will obtain necessary government regulatory approval or that any approved products will be commercially viable. Even if the Company’s product development efforts are successful, it is uncertain when, if ever, the Company will generate significant revenue from product sales. The Company operates in an environment of rapid technological change and substantial competition from other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. In addition, the Company is dependent upon the services of its employees, consultants and other third parties.
Segment Reporting
Operating segments are identified as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete financial information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision-maker in making decisions regarding resource allocation and assessing performance. The Company views its operations and manages its business in one operating segment.
Foreign Currency Translation and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company’s functional currency and reporting currency is the United States dollar. BBL’s functional currency is the Australian dollar (AUD). Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the reporting period. Equity transactions are translated at each historical transaction date spot rate. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a component of stockholders’ equity in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) for all periods presented consists entirely of foreign currency translation gains and losses.
Fair Value Measurements
The Company measures its financial assets and liabilities in accordance with GAAP using ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements. For certain financial instruments, including cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, the carrying amounts approximate fair value due to their short maturities.
10
The Company follows accounting guidance for financial assets and liabilities. ASC 820 defines fair value, provides guidance for measuring fair value and requires certain disclosures. The guidance utilizes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The following is a brief description of those three levels:
Level 1: |
|
Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
|
|
|
Level 2: |
|
Inputs, other than quoted prices that are observable, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active. |
|
|
|
Level 3: |
|
Unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore developed using estimates and assumptions developed by us, which reflect those that a market participant would use. |
As of December 31, 2025 and June 30, 2025, the Company had
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and at banks, short-term deposits with an original maturity of three months or less with financial institutions. There were no cash equivalents as of December 31, 2025 and June 30, 2025.
Restricted cash balances of $
Concentrations of Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to significant concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash. The Company maintains deposits at federally insured financial institutions in excess of federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts, and management believes that the Company is not exposed to significant credit risk due to the financial position of the depository institutions in which those deposits are held.
Trade and Other Receivables
The Company estimates current expected credit losses in accordance with ASC 326- Financial Instruments – Credit Losses on trade and other receivables on an ongoing basis, and will recognize those expected credit losses immediately. Estimates of current expected credit losses will be based on analyses of individual customer circumstances and historical write-off experience. The Company’s analyses will consider the aging of receivable accounts, customer creditworthiness, and general economic conditions.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals, and improvements are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation and amortization are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations.
Software |
|
|
Lab equipment |
|
|
Computer hardware |
|
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Property and equipment are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable.
11
Trade and other payables
These amounts represent liabilities for goods and services provided to the Company prior to the end of the period and which are unpaid. Due to their short-term nature, they are measured at cost and are not discounted. The amounts are unsecured and are usually paid within 30 days of recognition.
Leases
At lease commencement, the Company records a lease liability based on the present value of lease payments over the expected lease term. The Company calculates the present value of lease payments using the discount rate implicit in the lease, unless that rate cannot be readily determined. In that case, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate, which is the rate of interest that the Company would have to pay to borrow on a collateralized basis an amount equal to the lease payments over the expected lease term. The Company records a corresponding right-of-use lease asset based on the lease liability, adjusted for any lease incentives received and any initial direct costs paid to the lessor prior to the lease commencement date.
After lease commencement, the Company measures its leases as follows: (i) the lease liability based on the present value of the remaining lease payments using the discount rate determined at lease commencement; and (ii) the right-of-use lease asset based on the remeasured lease liability, adjusted for any unamortized lease incentives received, any unamortized initial direct costs and the cumulative difference between rent expense and amounts paid under the lease agreement. Any lease incentives received and any initial direct costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the expected lease term. Rent expense is recorded on a straight-line basis over the expected lease term.
Lease terms may include options to extend the lease when the Company is reasonably certain that it will exercise the option. Certain lease agreements may contain variable costs such as utilities and common area maintenance. Variable lease costs are expensed when the cost is incurred.
The Company elected the short-term lease practical expedient that allows entities to recognize lease payments on a straight-line basis over the lease term for leases with a term of 12 months or less. The Company has also elected the practical expedient under ASC Topic 842 allowing entities to not separate non-lease components from lease components, but instead account for such components as a single lease component for all leases.
Basic and Diluted Net Loss Per Share
Basic net loss per share is calculated by dividing net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net loss per share is calculated by dividing net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding plus potential common shares. Stock options, warrants and convertible instruments are considered potential common shares and are included in the calculation of diluted net loss per share using the treasury stock method when their effect is dilutive. Potential common shares are excluded from the calculation of diluted net income (loss) per share when their effect is anti-dilutive. As of December 31, 2025 and June 30, 2025, there were
Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding for the six months ended December 31, 2025 and 2024 include
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expenses relate primarily to the cost of conducting clinical and pre-clinical trials. Pre-clinical and clinical development costs are a significant component of research and development expenses. The Company records accrued liabilities for estimated costs of research and development activities conducted by third-party service providers, which include the conduct of pre-clinical studies and clinical trials, and contract manufacturing activities. The Company records the estimated costs of research and development activities based upon the estimated amount of services provided but not yet invoiced and includes these costs in trade and other payables on the consolidated balance sheets and within research and development expenses on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
The Company accrues for these costs based on factors such as estimates of the work completed and in accordance with agreements established with its third-party service providers. The Company makes significant judgments and estimates in determining the accrued
12
liabilities balance at the end of each reporting period. As actual costs become known, the Company adjusts its accrued liabilities. The Company has not experienced any material differences between accrued costs and actual costs incurred.
Share-based Compensation Expense
The Company records share-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Stock Compensation. ASC 718 requires the fair value of all share-based compensation awarded to employees and non-employees to be recorded as an expense over the shorter of the service period or the vesting period. The Company determines employee and non-employee share-based compensation based on the grant-date fair value using the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model.
Under ASC 718, the exercise price for share based compensation is determined using the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. For an award with graded vesting subject only to a service condition (e.g., time-based vesting), ASC 718-10-35-8 provides an accounting policy choice between graded vesting attribution or straight-line attribution. The Company elects the graded vesting method, recognizing compensation expense for only the portion of awards expected to vest. If an award is forfeited, The Company reverses compensation expense previously recognized in the period the award is forfeited.
Common Stock Warrants
The Company accounts for its common stock warrants in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (“ASC 480”) and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging (“ASC 815”). Based upon the provisions of ASC 480 and ASC 815, the Company accounts for common stock warrants as current liabilities if the warrant fails the equity classification criteria. The Company classifies certain warrants for the purchase of shares of its common stock as equity on its consolidated balance sheets as these warrants are considered indexed to the Company’s shares of common stock. For warrants that do not meet the criteria of a liability warrant and are classified on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as equity instruments, the Company uses the Black-Scholes model to measure the value of the warrants at issuance.
The pre-funded warrants are immediately exercisable at a price of $
Income Taxes
The Company is subject to Australia and United States income tax laws. The Company follows ASC 740, Accounting for Income Taxes, when accounting for income taxes, which requires an asset and liability approach to financial accounting and reporting for income taxes. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are computed annually for temporary differences between the financial statements and tax bases of assets and liabilities that will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future based on enacted tax laws and rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount more likely than not to be realized. For uncertain tax positions that meet a “more likely than not” threshold, the Company recognizes the benefit of uncertain tax positions in the consolidated financial statements. The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and penalties, if any, related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
13
Correction of Immaterial Errors
During the third quarter of 2025, the Company identified an immaterial error in the Company’s previously issued consolidated financial statements related to weighted-average number of common shares outstanding within the net loss per share computation. The error pertains to the exclusion of pre-funded warrants from the weighted-average number of common shares used in the computation of net loss per share. The Company assessed materiality, including qualitative and quantitative factors, and determined the error is immaterial to both the current and prior periods. The Company has revised the comparative net loss per share information as presented and disclosed within these consolidated financial statements. The revision had no effect on the consolidated balance sheet, consolidated statements of cash flows, consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity, or to reported net losses.
During the year ended June 30, 2025, the Company identified an immaterial error in the Company’s previously issued March 31, 2024 unaudited interim condensed consolidated, June 30, 2024 annual audited consolidated, and September 30, 2024 unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements related to the computation of share-based compensation expense resulting from inaccurate system configuration. The Company assessed materiality, including qualitative and quantitative factors, and determined the error is immaterial to the aforementioned prior periods. The Company has recorded a cumulative catch up out-of-period adjustment within the December 31, 2024 unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statement. Refer to our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025, for further information.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2023, the FASB issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) No. 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280) Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which requires disclosures about significant segment expenses and additional interim disclosure requirements. The standard also requires a single reportable segment company to provide all disclosures required by Topic 280. The Company adopted ASU 2023-07 during the year ended June 30, 2025. See Note 13 for the segment disclosures as required by Topic 280, as amended by ASU 2023-07.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards Not Yet Adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740) – Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which enhances the transparency, effectiveness, and comparability of income tax disclosures by requiring consistent categories and greater disaggregation of information related to income tax rate reconciliations and the jurisdictions in which income taxes are paid. This guidance is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024 with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the ASU on its income tax disclosures within the consolidated financial statements.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, ASC 220- Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures, as amended by ASU 2025-01 in January 2025, which requires entities, in the notes to financial statements, to disclose specified information about certain costs and expenses. The guidance is effective for the Company’s annual periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is assessing the impact of adopting this guidance on its consolidated financial statements.
In September 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-06 "Intangibles: Goodwill and Other‒Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Targeted Improvements to the Accounting for Internal-Use Software" to modernize the accounting for software costs under Subtopic 350-40, Intangibles‒Goodwill and Other‒Internal-Use Software (referred to as “internal-use software”). Upon adoption, we will be required to account for internal-use software under the updated capitalization criteria. The standard is effective for our interim and annual fiscal 2029 periods, with early adoption permitted. The standard can be applied either prospectively, retrospectively, or under a modified transition approach. We are currently assessing adoption timing and the effect that the ASU will have on our financial statements and disclosures.
In December 2025, the FASB issued ASU No. 2025-11, Interim Reporting (Topic 270): Narrow-Scope Improvements. The ASU clarifies interim disclosure requirements and the applicability of Topic 270. The objective of the amendments is to provide further clarity about the current interim disclosure requirements. The ASU is effective for interim reporting periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Adoption of this ASU can be applied either a prospective or a retrospective approach. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the provisions of this ASU and do not expect this ASU to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In December 2025, the FASB issued ASU No. 2025-12, Codification Improvements. The ASU addresses thirty-three items, representing the changes to the Codification that (1) clarify, (2) correct errors, or (3) make minor improvements. Generally, the amendments in this Update are not intended to result in significant changes for most entities. The ASU is effective for interim reporting periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026. The adoption method of this ASU may vary, on an issue-by-issue basis. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the provisions of this ASU and do not expect this ASU to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
14
3. Liquidity
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. For the six months ended December 31, 2025 and 2024, the Company incurred net losses of $
The Company’s business focuses on the development of novel genetic medicines and, at this stage in the Company’s development, the Company has not established a source of revenue to cover its full operating costs, and as such, is dependent on funding operations through capital financing activities. As of December 31, 2025, the Company had $
On October 11, 2024, we entered into a Sales Agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with Leerink Partners LLC (the “Agent”). Pursuant to the terms of the Sales Agreement, we may offer and sell shares of our common stock having an aggregate offering amount of up to $
On November 5, 2025, we entered into an Underwriting Agreement with Leerink Partners LLC and TD Securities (USA) LLC and Evercore Group L.L.C., as representatives of the several underwriters named therein, pursuant to which we agreed to issue and sell, in a firm commitment underwritten offering by us (the “November 2025 Underwritten Offering”),
Concurrently with the November 2025 Underwritten Offering, on November 5, 2025, we entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with affiliates of Suvretta Capital, Averill Master Fund, Ltd. and Averill Madison Master Fund, Ltd. (together, the “Purchasers” and the “Suvretta Funds”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers an aggregate of
We received gross proceeds from the Offerings of approximately $
We estimate that our cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to fund the Company’s operations for at least the next twelve months from the date of this report.
The Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon its ability to manage its net loss, become profitable, and obtain adequate financing. While the Company believes in its ability to generate revenue and raise additional funds, there can be no assurances to that effect. The financial statements do not include any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets or the amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern due to unsuccessful product development or commercialization, or the inability to obtain adequate financing in the future.
15
4. Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
Cash at bank |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
5. Prepaid and other assets
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
Prepaid expenses |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Market value of listed shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less:non-current portion |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Current portion |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
6. Property and equipment, net
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
Software |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Lab equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Computer hardware |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Leasehold improvements |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total property and equipment, gross |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total property and equipment, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Depreciation and amortization expense was $
7. Trade and other payables
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
Trade payable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued consultant fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued professional fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued clinical development project costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other payables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
8. Leases
The Company has entered into operating leases for offices in Hayward, California and Los Angeles, California. On February 1, 2025, the Company entered into a lease agreement to extend the lease in Hayward through to 2027. Similarly, on November 14, 2025, the Company entered into a lease agreement to extend the lease in Los Angeles through to 2028. Both extensions were recognized as a modification to the existing leases. The lease modifications were not accounted for as a separate contract and instead the existing operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities were remeasured during the period under agreements that expire in 2027 and 2028. Both leases contain options to extend for additional renewal periods. The leases require the Company to pay utilities, insurance, taxes, and other operating expenses. The Company’s lease does not contain any residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants.
16
The tables below show the changes during the six months ended December 31, 2025:
(US$’000) |
|
Operating |
|
|
Balance at July 1, 2025 |
|
$ |
|
|
Re-measurement during the period |
|
|
|
|
Amortization of right of use asset |
|
|
( |
) |
Operating lease right-of-use asset at December 31, 2025 |
|
$ |
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
Operating |
|
|
Balance at July 1, 2025 |
|
$ |
|
|
Re-measurement during the period |
|
|
|
|
Principal payments on operating lease liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
Operating lease liabilities at December 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
Less:non-current portion |
|
|
( |
) |
Current portion at December 31, 2025 |
|
$ |
|
|
As of December 31, 2025, the Company’s operating leases have a weighted average lease term of
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|
2026 |
|
$ |
|
|
2027 |
|
|
|
|
2028 |
|
|
|
|
Total operating lease payments |
|
|
|
|
Less imputed interest |
|
|
( |
) |
Present value of operating lease liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
The Company recorded lease liabilities and right-of-use lease assets for the lease based on the present value of lease payments over the expected lease term, discounted using the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. The incremental borrowing rate was determined based on quoted rates by the Company’s business banker for collateralized debt with terms similar to the lease agreements.
Rent expense was $
9. Stockholders’ equity
Preferred Stock
On December 6, 2024, the stockholders of the Company approved an amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, to authorize the issuance of
Common Stock
On December 8, 2021, the stockholders of the Company approved an amendment (the “Charter Amendment”) to the Company’s Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation to increase the total number of authorized shares of common stock of the Company from
17
On October 11, 2024, the Company entered into a Sales Agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with Leerink Partners LLC (the “Agent”). Pursuant to the terms of the Sales Agreement, the Company may offer and sell shares of the Company’s common stock having an aggregate offering amount of up to $
Concurrently with the March 2025 Underwritten Offering (as defined below), on March 25, 2025, the Company also entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement to which the Company issued and sold
On November 5, 2025, we entered into an Underwriting Agreement with Leerink Partners LLC and TD Securities (USA) LLC and Evercore Group L.L.C., as representatives of the several underwriters named therein, pursuant to which we agreed to issue and sell, in a firm commitment underwritten offering by us (the “November 2025 Underwritten Offering”),
Concurrently with the November 2025 Underwritten Offering, on November 5, 2025, we entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with affiliates of Suvretta Capital, Averill Master Fund, Ltd. and Averill Madison Master Fund, Ltd. (together, the “Purchasers” and the “Suvretta Funds”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers an aggregate of
Total gross proceeds received by the Company during the six-month period ended December 31, 2025 from the issuance of common stock totaled $
Warrants and Common Stock
On December 6, 2019, investors were issued
On September 15, 2022, we closed an underwritten public offering in which we issued and sold (i)
18
$
On August 11, 2023 we closed an underwritten public offering in which we sold
On April 22, 2024 we closed a private investment in public equity (PIPE) financing in which we sold
On August 29, 2024, the Company’s stockholders approved the exercise of certain existing warrants issued in April 2024, September 15, 2022 and August 11, 2023 in accordance with the rules of the Nasdaq Stock Market which otherwise would be subject to the Beneficial Ownership Limitation.
On March 25, 2025, the Company entered into an underwriting agreement to which the Company issued and sold (i)
As of December 31, 2025, there were
The activity related to warrants for the six months ended December 31, 2025, is summarized as follows:
|
|
Common |
|
|
Weighted- |
|
||
Outstanding at July 1, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Outstanding and exercisable at September 30, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Pre-funded warrants exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
Series 2 warrants exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
Outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Equity Incentive Plan
Employee Share Option Plan
In connection with its re-domiciliation to the United States, the Company assumed BBL’s obligations with respect to the settlement of options that were issued by BBL prior to the re-domiciliation pursuant to the Benitec Officers’ and Employees’ Share Option Plan (the “Plan”). This includes the Company’s assumptions of the Plan and all award agreements pursuant to which each of the options were
19
granted. Each option when exercised entitles the option holder to one share in the Company. Options are exercisable on or before an expiry date, do not carry any voting or dividend rights and are not transferable except on death of the option holder or in certain other limited circumstances. Employee options vest one third on each anniversary of the applicable grant date for three years. If an employee dies, retires, or otherwise leaves the organization, and certain other conditions have been satisfied, generally the employee has 12 months to exercise their options, or the options are cancelled. After the Re-domiciliation, no new options have been or will be issued under the Plan.
On July 1, 2024, the Plan and all options granted thereunder expired by its and their terms.
Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan
On December 9, 2020, the Company’s stockholders approved the Company’s 2020 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2020 Plan”). The 2020 Plan provides for the grant of various equity awards. Currently, only stock options are outstanding under the 2020 Plan. Each option when exercised entitles the option holder to one share of the Company’s common stock. Options are exercisable on or before an expiry date, do not carry any voting or dividend rights, and are not transferable except on death of the option holder or in certain other limited circumstances. Employee stock options vest in increments of one-third on each anniversary of the applicable grant date over three years. Non-employee director options vest in increments of one-third on the day prior to each of the Company’s next three annual stockholder meetings following the grant date. Executive Options granted on December 9, 2024, and December 27, 2024, vest in sixteen substantially equal quarterly installments on the last day of each full fiscal quarter of the Company ending after the grant date. If an option holder dies or terminates employment or service due to Disability (as defined in the 2020 Plan), the option holder generally has 12 months to exercise their vested options, or the options are cancelled. If an option holder otherwise leaves the Company, other than for a termination by the Company for Cause (as defined in the 2020 Plan), the option holder generally has 90 days to exercise their vested options, or the options are cancelled. The maximum contractual term of options granted under the 2020 Plan is
On December 8, 2021, the Company’s stockholders approved an amendment to the 2020 Plan, which increased the number of shares of the Company’s common stock reserved under the 2020 Plan to
Equity Awards
The activity related to equity awards, which are comprised of stock options during the six months ended December 31, 2025 is summarized as follows:
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
Aggregate |
|
||||
Outstanding at June 30, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding at December 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Equity-based Compensation Expense
The Company estimated the fair value of each employee equity award on the grant date using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following assumptions:
20
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||
Expected volatility |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Expected term |
|
|
|
|
||||
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
— |
% |
|
|
— |
% |
Expected Volatility. The Company has based its estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of the price of its common stock. The Company computed historical volatility data using the daily closing prices for its shares during the equivalent period of the calculated expected term of the equity-based awards.
Expected Term. The expected term represents the period that the equity awards are expected to be outstanding. For stock options with service conditions, it is based on the “simplified method” for developing the estimate of the expected life. Under this approach, the expected term is presumed to be the midpoint between the average vesting date and the end of the contractual term.
Risk-free Interest Rate. The Company bases the risk-free interest rate assumption on U.S. Treasury constant maturities with maturities similar to those of the expected term of the equity award being valued.
Expected Dividend Yield. The Company bases the expected dividend yield assumption on the fact that it has never paid dividends and does not expect to pay dividends in the foreseeable future.
In addition to assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, the Company accounts for forfeitures of share-based awards as they occur.
Share-Based Compensation Expense
The classification of share-based compensation expense is summarized as follows:
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
(US$’000) |
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||||
Research and development |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
General and administrative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Total share-based compensation expense |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
As of December 31, 2025, there was $
10. Income taxes
For the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, and December 31, 2024, respectively, the Company did not recognize a provision or benefit for income taxes as it has incurred net losses. In addition, the net deferred tax assets generated from net operating losses are fully offset by a valuation allowance as the Company believes it is not more likely than not that the benefit will be realized.
11. Commitments and contingencies
Contract commitments
The Company enters into contracts in the normal course of business with third-party contract research organizations, contract development and manufacturing organizations and other service providers and vendors. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice and, therefore, are cancellable contracts and not considered contractual obligations and commitments.
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company may become subject to claims and litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company is not a party to any material legal proceedings, nor is it aware of any material pending or threatened litigation.
21
12. Segment reporting
The Company’s operating segments are components of the Company for which separate discrete financial information is available and is evaluated by the Company’s chief operating decision maker (“CODM”), the , in deciding how to allocate resources and assess performance. The Company’s CODM views the Company’s operations and manages its business as a reportable segment with a operating segment,
While the Company has subsidiaries in several geographic regions, there are no standalone operations; rather, all R&D activities are supported by a single corporate team. The determination of a single reportable segment is consistent with the consolidated financial information available and regularly reviewed by the Company’s CODM. The Company manages R&D activities and operating expenses on a consolidated basis.
The results of the Company’s reportable segment is summarized as follows:
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
||||||||||
(US$’000) |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
Operating Expenses |
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||||
Research and development |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
General and administrative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Other segment items |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Other segment items include foreign currency transaction loss (gain), interest expense (income), net loss (gain) on extinguishment of liabilities, and other expense (income).
13. Related party transactions
During the three and six months ended December 31, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the Company did not enter into any related party transactions other than as set forth below or equity and other compensation, termination, change in control and other arrangements, which are described or incorporated by reference in Part III of the June 30, 2025 Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On September 26, 2024, Suvretta Capital, on behalf of itself and each of the Suvretta Funds (as defined below), entered into a waiver with the Company, pursuant to which, among other things (i)
On November 5, 2025, the Company sold
22
Item 2. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
You should read the following discussion and analysis of financial condition and operating results together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes and other financial information included elsewhere in this document.
Company Overview
We endeavor to become the leader in discovery, development, and commercialization of therapeutic agents capable of addressing significant unmet medical need via the application of the silence and replace approach to the treatment of genetic disorders.
Benitec Biopharma Inc. (“Benitec” or the “Company” or in the third person, “we” or “our”) is a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on the advancement of novel genetic medicines with headquarters in Hayward, California. The proprietary platform, called DNA-directed RNA interference, or ddRNAi, combines RNA interference, or RNAi, with gene therapy to create medicines that facilitate sustained silencing of disease-causing genes following a single administration. The unique therapeutic constructs also enable the simultaneous delivery of functional replacement genes, facilitating the proprietary “silence and replace” approach to the treatment of genetically defined diseases. The Company is developing a silence and replace-based therapeutic (BB-301) for the treatment of Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy (OPMD), a chronic, life-threatening genetic disorder.
BB-301 is a silence and replace-based genetic medicine currently under development by Benitec. BB-301 uses DNA-directed RNA interference (ddRNAi) to simultaneously silence the mutant gene and replace it with a functional gene, potentially providing a permanent solution with a single administration. This fundamental therapeutic approach to disease management is called “silence and replace.” The silence and replace mechanism offers the potential to restore the normative physiology of diseased cells and tissues and to improve treatment outcomes for patients suffering from the chronic, and potentially fatal, effects of OPMD. BB-301 has been granted Orphan Drug Designation in the United States and the European Union.
This differentiated platform, whereby we combine the gene-silencing effects of RNAi with the durable transgene expression achievable by using a single-vector approach provides the silence and replace approach with the potential to permanently silence the mutant gene that causes OPMD and deliver a healthy, functional gene in its place following a single administration of the proprietary genetic medicine. We believe that this novel mechanistic profile of the current and future investigational agents developed by Benitec could facilitate the achievement of robust and durable clinical activity while greatly reducing the frequency of drug administration traditionally expected for medicines employed for the management of chronic diseases. Additionally, the achievement of permanent gene silencing and gene replacement may significantly reduce the risk of patient non-compliance during the course of medical management of potentially fatal clinical disorders.
We will require additional financing to progress our product candidates through to key inflection points.
ddRNAi is designed to produce permanent silencing of disease-causing genes, by combining RNA interference, or RNAi, with viral delivery agents typically associated with the field of gene therapy (i.e., viral vectors). Modified AAV vectors are employed to deliver genetic constructs which encode short hairpin RNAs that are, then, serially expressed and processed to produce siRNA molecules within the transduced cell for the duration of the life of the target cell. These newly introduced siRNA molecules drive permanent silencing of the expression of the disease-causing gene. The silence and replace approach further bolsters the biological benefits of permanent silencing of disease-causing genes by incorporating multifunctional genetic constructs within the modified AAV vectors to create an AAV-based gene therapy agent that is designed to silence the expression of disease-causing genes (to slow, or halt, the underlying mechanism of disease progression) and to simultaneously replace the mutant genes with normal, functional genes (to drive restoration of function in diseased cells). This fundamentally distinct therapeutic approach to disease management offers the potential to restore the underlying physiology of the treated tissues and, in the process, improve treatment outcomes for patients suffering from the chronic and, potentially, fatal effects of diseases like Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy (OPMD).
Traditional gene therapy is defined by the introduction of an engineered transgene to correct the pathophysiological derangements derived from mutated or malfunctioning genes. Mutated genes can facilitate the intracellular production of disease-causing proteins or hamper the production of critical, life-sustaining, proteins. The introduction of a new transgene can facilitate the restoration of production of normal proteins within the diseased cell, thus restoring natural biological function. Critically, the implementation of this traditional method of gene therapy cannot eliminate the expression, or the potential deleterious effects of, the underlying mutant gene (as mutant proteins may be continually expressed and aggregate or drive the aggregation of other native proteins within the diseased cell). In this regard, the dual capabilities of the proprietary silence and replace approach to silence a disease-causing gene via ddRNAi and
23
simultaneously replace the functional activity of a mutant gene via the delivery of an engineered transgene could facilitate the development of differentially efficacious treatments for a range of genetic disorders.
Overview of RNAi and the siRNA Approach
The mutation of a single gene can cause a chronic disease via the resulting intracellular production of a disease-causing protein (i.e., an abnormal form of the protein of interest), and many chronic and/or fatal disorders are known to result from the inappropriate expression of a single gene or multiple genes. In some cases, genetic disorders of this type can be treated exclusively by “silencing” the intracellular production of the disease-causing protein through well-validated biological approaches like RNA interference (“RNAi”). RNAi employs small nucleic acid molecules to activate an intracellular enzyme complex, and this biological pathway temporarily reduces the production of the disease-causing protein. In the absence of the disease-causing protein, normal cellular function is restored and the chronic disease that initially resulted from the presence of the mutant protein is partially or completely resolved. RNAi is potentially applicable to over 20,000 human genes and a large number of disease-causing microorganism-specific genes.
Figure 1
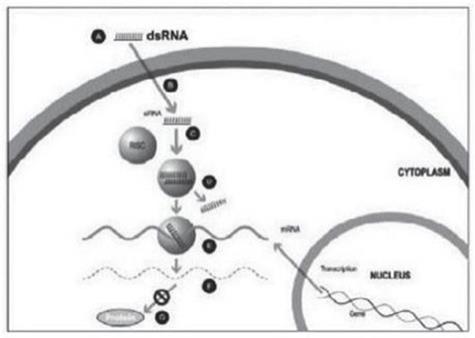
A small double stranded RNA, or dsRNA, molecule (A, Figure 1), comprising one strand known as the sense strand and another strand known as the antisense strand, which are complementary to each other, is synthesized in the laboratory. These small dsRNAs are called small interfering RNAs, or siRNAs. The sequence of the sense strand corresponds to a short region of the target gene mRNA. The siRNA is delivered to the target cell (B, Figure 1), where a group of enzymes, referred to as the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex, or RISC, process the siRNA (C, Figure 1), where one of the strands (usually the sense strand) is released (D, Figure 1). RISC uses the antisense strand to find the mRNA that has a complementary sequence (E, Figure 1) leading to the cleavage of the target mRNA (F, Figure 1). As a consequence, the output of the mRNA (protein production) does not occur (G, Figure 1). Several companies, including Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc. (“Alnylam”), utilize this approach in their RNAi product candidates.
Importantly, many genetic disorders are not amenable to the traditional gene silencing approach outlined in Figure 1, as the diseased cells may produce a mixture of the functional protein of interest and the disease-causing mutant variant of the protein, and the underlying genetic mutation may be too small to allow for selective targeting of the disease-causing variant of the protein through the use of siRNA-based approaches exclusively. In these cases, it is extraordinarily difficult to selectively silence the disease-causing protein without simultaneously silencing the functional intracellular protein of interest whose presence is vital to the conduct of normal cellular functions.
24
Our proprietary silence and replace technology utilizes the unique specificity and robust gene silencing capabilities of RNAi while overcoming many of the key limitations of siRNA-based approaches to disease management.
In the standard RNAi approach, double-stranded siRNA is produced synthetically and, subsequently, introduced into the target cell via chemical modification of the RNA or alternative methods of delivery. While efficacy has been demonstrated in several clinical indications through the use of this approach, siRNA-based approaches maintain a number of limitations, including:
Our Approach to the Treatment of Genetic Diseases—ddRNAi and Silence and Replace
Our proprietary silence and replace approach to the treatment of genetic diseases combines RNAi with functional gene replacement to permanently silence the mutant genes and replace with functional genes potentially providing a permanent solution with a single administration of the therapeutic agent. Benitec employs ddRNAi in combination with classical gene therapy (i.e., transgene delivery via viral vectors) to overcome several of the fundamental limitations of RNAi.
The silence and replace approach to the treatment of genetic disorders employs adeno-associated viral vectors (“AAVs”) to deliver genetic constructs which may, after a single administration to the target tissues:
Our silence and replace technology utilizes proprietary DNA expression cassettes to foster continuous production of gene silencing shRNAs and functional proteins (via expression of the functional transgene). A range of viral gene therapy vectors can be used to deliver the DNA construct into the nucleus of the target cell and, upon delivery, shRNA molecules are expressed and subsequently processed by intracellular enzymes into siRNA molecules that silence the expression of the mutant, disease-causing protein (Figure 2).
In the silence and replace approach (Figure 2):
25
Figure 2
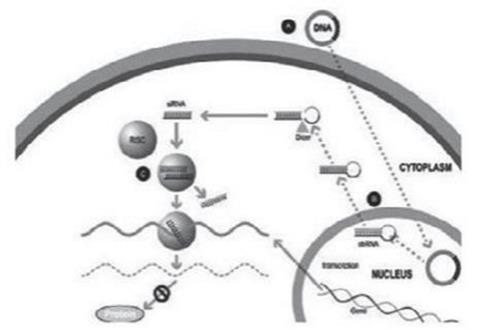
Our strategy is to discover, develop and commercialize treatments that leverage the capabilities of ddRNAi and the silence and replace approach to disease management.
For selected product candidates, at the appropriate stage, we may collaborate with large biopharmaceutical companies to further co-develop and, if approved, commercialize our ddRNAi-based and silence and replace-based products to achieve broad clinical and commercial distribution. For specific clinical indications that we deem to be outside of our immediate areas of focus, we will continue to out-license, where appropriate, applications of our ddRNAi and silence and replace technology to facilitate the development of differentiated therapeutics, which could provide further validation of our proprietary technology and approach to disease management.
Our cash and cash equivalents will be deployed for the advancement of our product candidate BB-301 for the treatment of OPMD-derived dysphagia, including the natural history lead-in study and the Phase 1b/2a BB-301 treatment study, for the continued advancement of development activities for other existing and new product candidates, for general corporate purposes and for strategic growth opportunities.
Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy—OPMD
OPMD is an insidious, autosomal-dominant, late-onset degenerative muscle disorder that typically presents in patients at 40-to-50 years of age. The disease is characterized by progressive swallowing difficulties (dysphagia), eyelid drooping (ptosis) and limb weakness. OPMD is caused by a specific mutation in the poly(A)-binding protein nuclear 1, or PABPN1, gene. OPMD is a rare disease; however, patients have been diagnosed with OPMD in approximately 35 countries. Patient populations suffering from OPMD are well-identified, and significant geographical clustering has been noted for patients with this disorder, which could simplify clinical development and global commercialization efforts.
26
Our Pipeline
The following table sets forth our current product candidate and the development status:
Table 1. Pipeline: Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy

The Investigational New Drug (IND) application for BB-301 was approved to proceed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in June 2023. The first study subject was safely treated in Cohort 1 of the BB-301 Phase 1b/2a clinical trial (NCT06185673) in November 2023. Cohort 1 dosing was safely completed in the second calendar quarter of 2025. Cohort 2 dosing was safely initiated in the fourth calendar quarter of 2025 . BB-301 is the lead investigational gene therapy agent under development by Benitec. BB-301 has been granted Orphan Drug Designation in the United States and the European Union and the key attributes of BB-301 are outlined in Figure 3.
Figure 3
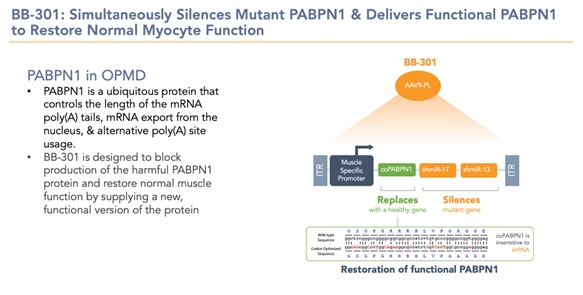
PABPN1 is a ubiquitous factor that promotes the interaction between the poly(A) polymerase and CPSF (cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor) and, thus, controls the length of mRNA poly(A) tails, mRNA export from the nucleus, and alternative poly(A) site usage. The characteristic genetic mutation underlying OPMD results in trinucleotide repeat expansion(s) within exon 1 of PABPN1 and results in an expanded poly-alanine tract at the N-terminal end of PABPN1. The mutation generates a protein with an N-terminal expanded poly-alanine tract of up to 18 contiguous alanine residues, and the mutant protein is prone to the formation of intranuclear
27
aggregates designated as intranuclear inclusions (INIs). The INIs that sequester functional PABPN1 may contribute to the “loss of function” phenotype associated with OPMD.
There are currently no therapeutic interventions approved for OPMD. BB-301 is the only clinical-stage therapeutic agent in development designed to treat dysphagia in patients with OPMD. Additionally, there are no surgical interventions available to OPMD patients that modify the natural history of the disease, which is principally comprised of chronic deterioration of swallowing function. BB-301 has received Orphan Drug Designation in the United States and the European Union and, upon achievement of regulatory approval for BB-301 in these respective jurisdictions, the Orphan Drug Designations would provide commercial exclusivity independent of intellectual property protection. While OPMD is a rare disorder, we believe the commercial opportunity for a safe and efficacious therapeutic agent in this clinical indication exceeds $1 billion over the course of the commercial life of the product.
BB-301 is our Lead, Silence and Replace-Based, OPMD Therapeutic Agent
BB-301 is composed of a modified AAV serotype 9 (AAV9) capsid that expresses a bifunctional construct under the control of a single muscle specific Spc5-12 promoter to achieve co-expression of both the codon-optimized PABPN1 mRNA and two shmiR molecules directed against functional and mutant PABPN1. BB-301 is designed to correct the genetic defect underlying OPMD following a single localized administration.
BB-301—Design and Mechanism of Action
BB-301 is designed to target two distinct regions of the PABPN1 mRNA to accomplish gene silencing via the concomitant expression of two distinct shmiRs from a single DNA construct (Figure 3). BB-301 is also engineered to drive the simultaneous expression of a codon-optimized, siRNA-resistant, version of the functional PABPN1 gene (Figure 3).
Summary of the Key Regulatory Interactions:
Operational Updates
The key milestones related to the development of BB-301 for the treatment of OPMD, along with other corporate updates, are outlined below:
BB-301 Clinical Development Program Overview:
28
All six subjects in Cohort 1 have been safely treated with BB-301, and the first subject of Cohort 2 has been safely treated with BB-301.No treatment-related Severe Adverse Events have been observed for the Subjects treated with BB-301.
Interim Clinical Study Results and FDA Fast Track Designation
On January 11, 2026, we announced updated positive long-term clinical results for BB-301 Phase 1b/2a Clinical Trial. The first patient treated in Cohort 1 of the trial has completed the 24-month post-treatment assessment. These results serve as an update to the interim clinical results shared on November 3, 2025 that announced Cohort 1 patients demonstrated significant and sustained improvements across multiple clinical measures including dysphagic symptom burden, post-swallow residue accumulation, time required to consume fixed volumes of liquid, as well as improved pharyngeal closure during swallowing. The update provided in January 2026, shows that following the administration of BB-301, patient 1 in Cohort 1 continued to demonstrate robust, disease-modifying outcomes across multiple clinical measures including post-swallow residue at 24 months. Additionally, the first 4 patients in Cohort 1 have now completed the 12-month statistical follow-up period and continued to demonstrate durable response to BB-301. We look forward to engaging the U.S. Food and Drug Administration mid-2026 to confirm the BB-301 pivotal study design. BB-301 was previously granted fast track and Orphan Drug Designation in the U.S. and Orphan Drug Designation in the European Union (EU) for the treatment of OPMD with dysphagia.
Manufacturing
The manufacture of the biological products required for gene therapy is complex and difficult. We do not currently own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of preclinical, clinical or commercial quantities of any of our product candidates. We are exploring long-term manufacturing alliances with a number of potential partners to investigate manufacturing processes in order to produce materials at reasonable scale and cost of goods to support future commercialization efforts. We do not have a long-term agreement with any third-party manufacturer, but we plan to establish such a relationship with an appropriate manufacturer to serve our long-term needs.
29
Manufacturing is subject to extensive regulations that impose various procedural and documentation requirements, which govern record keeping, manufacturing processes and controls, personnel, quality control and quality assurance, among others. Our contract manufacturing organizations manufacture our product candidates under cGMP conditions. cGMP is a regulatory standard for the production of pharmaceuticals that will be used in humans.
Sales and Marketing
We have not yet established sales, marketing or product distribution operations because our product candidates are in preclinical or clinical development. If we receive marketing and commercialization approval for any of our product candidates, we intend to market the product through strategic alliances and distribution agreements with third parties. In certain cases, we may market an approved product directly worldwide or in selected geographical segments. The ultimate implementation of our strategy for realizing the financial value of our product candidates is dependent on the results of clinical trials for our product candidates, the availability of funds and the ability to negotiate acceptable commercial terms with third parties.
Competition
The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by intense and dynamic competition to develop new technologies and proprietary therapies.
Any product candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize will have to compete with existing therapies and new therapies that may become available in the future. While we believe that our proprietary technology and scientific expertise in gene silencing using ddRNAi provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from many different sources, including larger and better-funded pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, as well as from academic institutions and governmental agencies and public and private research institutions that may develop potentially competitive products or technologies. We are aware of several companies focused on developing gene therapy or gene silencing product candidates.
We are not aware of any companies developing a gene therapy or gene silencing approach for OPMD. Our product candidates, if approved, would also compete with treatments that have already been approved and accepted by the medical community, patients and third-party payers.
Many of our competitors and potential competitors, alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do and significantly greater experience in the discovery and development of product candidates, obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals of treatments and the commercialization of those treatments. Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. These competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel and establishing clinical study sites and subject registration for clinical studies, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies.
We anticipate that we will face intense and increasing competition as new products enter the market and advanced technologies become available. We expect any treatments that we develop and commercialize to compete on the basis of, among other things, efficacy, safety, convenience of administration and delivery, price, the level of competition and the availability of reimbursement from government and other third party-payers.
Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any products that we may develop. Our competitors also may obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain approval for ours, which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market. In addition, we expect that our therapeutic products, if approved, will be priced at a significant premium over competitive products and our ability to compete may be affected in many cases by insurers or other third-party payers seeking to encourage the use of competitive products including biosimilar or generic products.
This increasingly competitive landscape may compromise the development of our product candidates.
30
Foreign Currency Translation and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company’s functional currency and reporting currency is the United States dollar. BBL’s functional currency is the Australian dollar (AUD). Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the reporting period. Equity transactions are translated at each historical transaction date spot rate. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a component of stockholders’ equity in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) for all periods presented consists entirely of foreign currency translation gains and losses.
Results of Operations
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses relate primarily to the cost of conducting clinical and preclinical trials. Preclinical and clinical development costs are a significant component of research and development expenses. We record accrued liabilities for estimated costs of research and development activities conducted by third-party service providers, which include the conduct of preclinical studies and clinical trials, and contract manufacturing activities. We record the estimated costs of research and development activities based upon the estimated amount of services provided but not yet invoiced and includes these costs in trade and other payables on the consolidated balance sheets and within research and development expenses on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries, related benefits, travel, and equity-based compensation expense. General and administrative expenses also include facility expenses, professional fees for legal, consulting, accounting and audit services and other related costs.
We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses may increase as we focus on the continued development of the clinical OPMD program. We also anticipate an increase in expenses relating to accounting, legal and regulatory-related services associated with maintaining compliance with exchange listing and SEC requirements, director and officer insurance premiums and other similar costs.
Operating Expenses
The following tables sets forth a summary of our expenses for each of the periods:
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||||
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
|||||||||||||
Operating Expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Research and development |
|
$ |
5,834 |
|
|
$ |
5,385 |
|
|
$ |
9,204 |
|
|
$ |
8,970 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
7,543 |
|
|
|
5,420 |
|
|
|
13,976 |
|
|
|
7,626 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
$ |
13,377 |
|
|
$ |
10,805 |
|
|
$ |
23,180 |
|
|
$ |
16,596 |
|
During the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, we incurred $5.8 million and $9.2 million in research and development expenses, respectively, as compared to $5.4 million and $9.0 million for the comparable period ended December 31, 2024. Research and development expenses relate primarily to ongoing clinical development of BB-301 for the treatment of OPMD. The increase for the three and six months ended December 31, 2025 reflects increase in share based compensation of $2.2 million and $3.0 million, respectively, offset by the timing of contract manufacturing activity and the timing of payments for the OPMD Natural History and Dosing study.
General and administrative expense totaled $7.5 million and $14.0 million for the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, compared to $5.4 million and $7.6 million for the comparable period ended December 31, 2024. The increase for the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, relates primarily to an increase in share based compensation of $2.0 million and $6.0 million and salaries and wages of $0.6 million and $0.9 million, offset by a decrease in legal fees of $0.4 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
31
Other Income (Expense)
The following tables sets forth a summary of our other income (loss) for each of the periods:
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
||||||||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||||
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
|||||||||||||
Other Income (Loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Foreign currency transaction gain (loss) |
|
$ |
131 |
|
|
$ |
(294 |
) |
|
$ |
42 |
|
|
$ |
(201 |
) |
Interest income, net |
|
|
1,390 |
|
|
|
823 |
|
|
|
2,401 |
|
|
|
1,427 |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
|
(65 |
) |
|
|
(5 |
) |
Gain on extinguishment of liabilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
764 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
764 |
|
Total other income (loss), net |
|
$ |
1,540 |
|
|
$ |
1,253 |
|
|
$ |
2,378 |
|
|
$ |
1,985 |
|
Other income (loss), net during the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, which consists of foreign currency transaction gain (loss), interest income, and other income (expense), net, totaled $1.5 million and $2.4 million, respectively. Other income (loss), net during the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, consists of foreign currency transaction gain (loss), interest income, and other expense, net, totaled $1.3 million and $2.0 million, respectively. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses reflect changes in foreign exchange rates. Net interest income for the three and six months ended December 31, 2025, in comparison to the three and six months ended December 31, 2024, reflects the increase in the Company’s cash and cash equivalent balances. Gain on extinguishment of liabilities is due to the settlement with a vendor of an outstanding trade payable balance and an accrued clinical development project cost balance totaling $1.3 million for $0.5 million due to a dispute regarding contract performance and deliverables. This settlement resulted in a gain of $0.8 million in the three and six months ended December 31, 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company has incurred cumulative losses and negative cash flows from operations since our predecessor’s inception in 1995. The Company had accumulated losses of $249 million as of December 31, 2025. We expect that our research and development expenses will increase due to the continued development of the OPMD program.
As of December 31, 2025, we do not have outstanding borrowings or credit facilities.
As of December 31, 2025, the Company has issued warrants allowing holders to purchase 20,179,428 shares of Common Stock, consisting of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
September 2022 Pre-Funded Warrants to purchase Common |
|
|
588,236 |
|
|
|
588,236 |
|
Series 2 Warrants to purchase Common Stock |
|
|
37,745 |
|
|
|
101,537 |
|
August 2023 Pre-Funded Warrants to purchase Common |
|
|
12,179,739 |
|
|
|
12,179,739 |
|
Common Warrants to purchase Common Stock |
|
|
5,071,148 |
|
|
|
5,071,148 |
|
April 2024 Pre-Funded Warrants to purchase Common Stock |
|
|
2,002,560 |
|
|
|
2,202,836 |
|
March 2025 Pre-Funded Warrants to purchase Common |
|
|
300,000 |
|
|
|
300,000 |
|
Total |
|
|
20,179,428 |
|
|
|
20,443,496 |
|
32
As of December 31, 2025, we had cash and cash equivalents of approximately $188.8 million. Cash in excess of immediate requirements is invested in accordance with our investment policy, primarily with a view to liquidity and capital preservation. Currently, our cash and cash equivalents are held in bank accounts.
On October 11, 2024, we entered into the Sales Agreement disclosed above which provides for the sale of up to $75 million of our common stock from time-to-time in “at-the-market offerings”.
The following table sets forth a summary of the net cash flow activity for each of the periods set forth below:
|
|
Six Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2025 |
|
|
2024 |
|
||
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
|||||
Net cash provided by (used in): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating activities |
|
$ |
(7,127 |
) |
|
$ |
(12,289 |
) |
Investing activities |
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
|
(12 |
) |
Financing activities |
|
|
98,230 |
|
|
|
39,527 |
|
Effects of exchange rate changes on cash and cash |
|
|
(46 |
) |
|
|
190 |
|
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents, and |
|
$ |
91,046 |
|
|
$ |
27,416 |
|
Operating activities
Net cash used in operating activities for the six months ended December 31, 2025 and 2024 was $7.1 million and $12.3 million, respectively. Net cash used in operating activities was primarily the result of our net loss, partially offset by non-cash expenses, and changes in working capital primarily in trade and other payables.
Investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities six months ended December 31, 2025 and 2024 was $11 thousand and $12 thousand, respectively.
Financing activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $98.2 million and $39.5 million for the six months ended December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively. The financing activities for the six months ended December 31, 2025 primarily related to the issuance of common stock with gross proceeds of $104.5 million, offset by $6.3 million in share issuance costs. Cash from financing activities in the six months ended December 31, 2024 was related to the issuance of common stock from the exercise of Series 2 warrants and common stock warrants with gross proceeds of $39.5 million.
The future of the Company as an operating business will depend on its ability to manage operating costs and budgeted amounts and obtain adequate financing. While we continue to progress discussions and advance opportunities to engage with pharmaceutical companies and continue to seek licensing partners for ddRNAi in disease areas that are not our focus, there can be no assurance as to whether we will enter into such arrangements or what the terms of any such arrangement could be.
We do not have any products approved for sale and have not generated any revenue from product sales. We do not know when, or if, we will generate any revenue from product sales. We do not expect to generate significant revenue from product sales unless and until we obtain regulatory approval of and commercialize one of our current or future product candidates.
Unless and until we establish significant revenues from licensing programs, strategic alliances or collaboration arrangements with pharmaceutical companies, or from product sales, we anticipate that we will continue to generate losses for the foreseeable future, and we expect the losses to increase as we continue the development of product candidates and begin to prepare to commercialize any product that receives regulatory approval. We are subject to the risks inherent in the development of new gene therapy products, and we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays, and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business. We estimate that our cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to fund the Company’s operations for at least the next twelve months from the date of this report.
33
We have based our projections of operating capital requirements on assumptions that may prove to be incorrect and we may use all of our available capital resources sooner than we expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with research, development, and commercialization of pharmaceutical products, we are unable to estimate the exact amount of our operating capital requirements. Our future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
On October 1, 2016, the Company entered into an operating lease for office space in Hayward, California with multiple amendments extending the lease through December 2027. The Company also entered into a new lease in Los Angeles, California for office space with an initial expiration date in July 2026. The Company entered into a lease amendment for the Los Angeles office that extended the lease through January 2028. See Note 8 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q.
The Company enters into contracts in the normal course of business with third-party contract research organizations, contract development and manufacturing organizations and other service providers and vendors. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice and, therefore, are cancellable contracts and not considered contractual obligations and commitments.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Accounting Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make judgments, assumptions and estimates that affect the amounts reported. Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q describes the significant accounting policies used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. Certain of these significant accounting policies are considered to be critical accounting policies.
A critical accounting policy is defined as one that is both material to the presentation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements and requires management to make difficult, subjective, or complex judgments that could have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations. Specifically, these policies have the following attributes: (1) the Company is required to make assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time of the estimate; and (2) different estimates the Company could reasonably have used, or changes in the estimate that are reasonably likely to occur, would have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Estimates and assumptions about future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions believed to be applicable and reasonable under the circumstances. These estimates may change as new events occur, as additional information is obtained and as the Company’s operating environment changes. These changes have historically been minor and have been included in the consolidated financial statements as soon as they became known. In addition, management is periodically faced with uncertainties, the outcomes of which are not within its control and will not be known for prolonged periods of time. These uncertainties are discussed in the section above entitled “Risk Factors.” Based on a critical assessment of its accounting policies and the underlying judgments and uncertainties affecting the application of those policies, management believes that the Company’s consolidated financial statements are fairly stated in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and provide a meaningful presentation of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
34
Management believes that the following are critical accounting policies:
Research and Development Expense
Preclinical and clinical trial costs are a significant component of our research and development expenses. We accrue for preclinical and clinical development costs based on factors such as estimates of the work completed and in accordance with agreements established with our third-party service providers. We make significant judgments and estimates in determining the accrued liabilities balance at the end of each reporting period. As actual costs become known, we adjust our accrued liabilities accordingly on a prospective basis and will do so in the period in which the facts that give rise to the revision become reasonably certain.
Share-based Compensation Expense
We record share-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Stock Compensation. ASC 718 requires the fair value of all share-based employee compensation awarded to employees and non-employees to be recorded as an expense over the shorter of the service period or the vesting period. We determine employee and non-employee share-based compensation based on grant-date fair value using the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model and allocate the resulting compensation expense over the corresponding requisite service period using the graded vesting attribution method. We account for forfeitures of share-based awards as they occur.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements that we have adopted and have not yet adopted, see Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide the information pursuant to this Item.
Item 4. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We have established disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended). As of the end of the period covered by this Report we carried out an evaluation under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial and accounting officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures pursuant to Rule 13a-15 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Based on this evaluation, we reported a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting further described in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting in Item 9A of our Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025 relating to inadequate design and implementation of controls over our share-based compensation calculation review process; specifically, we did not design and/or implement process level controls to ensure all inputs used in share-based compensation expense calculations are complete and accurate, including review of the vesting allocation method applied by the equity system.
Our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that as of June 30, 2025, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective to provide reasonable assurance that information we are required to disclose in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
We do not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal controls will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected.
Remediation of Previously Reported Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
As reported in Part II, Item 9A, Controls and Procedures, of our Annual Reports on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025, filed on September 22, 2025, we previously identified a material weakness in our internal controls resulting from the inadequate design and implementation over our share-based compensation calculation review process.
35
Throughout the fiscal quarters ended September 30, 2025 and December 31, 2025, under the oversight of the audit committee, our management has designed and implemented new or enhanced internal control procedures, which we believe both address the identified material weakness and strengthens our overall financial control environment. Specifically, we have updated the equity system’s default vesting allocation method configuration and have established enhancements to our quarterly share-based compensation review process to identify and verify all relevant inputs of the share-based compensation expense calculation, including review over the completeness and accuracy of the vesting allocation method applied by the equity system.
Our management has completed the implementation of significant enhancements to our procedures and newly implemented controls. Based on these procedures and results of our testing of the implemented controls, we believe that the previously reported material weakness related to the inadequate design and implementation of controls over our share-based compensation calculation review process has been remediated. However, completion of remediation procedures for this material weakness does not provide assurance that our modified controls will continue to operate properly or that our financial statements will be free from error.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Other than the efforts towards remediating the material weakness as previously described above, there were no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2025 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
36
PART II
OTHER INFORMATION
Item 1. Legal Proceedings
We are currently not a party to any material legal proceedings.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
There have been no material changes to the risk factors disclosed in Item 1A of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025.
Item 2. Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
None.
Item 3. Defaults Upon Senior Securities
None.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
None.
Item 5. Other Information
During the quarter ended December 31, 2025,
37
Item 6. Exhibits.
Number |
|
Description of Document |
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
31.1 |
|
Statement of CEO Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002* |
|
|
|
31.2 |
|
Statement of CFO Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002* |
|
|
|
32.1 |
|
Statement of CEO Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002** |
|
|
|
32.2 |
|
Statement of CFO Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002** |
|
|
|
101.INS |
|
Inline XBRL Instance Document–the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File as its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document |
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema With Embedded Linkbase Documents |
|
|
|
104 |
|
Cover page formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101 |
* Filed herewith.
** Furnished, not filed.
38
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on our behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
Benitec Biopharma Inc. |
|
|
|
Dated: February 12, 2026 |
|
/s/ Jerel Banks |
|
|
Dr. Jerel Banks |
|
|
Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
(principal executive officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Megan Boston |
|
|
Megan Boston |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer and Secretary (principal financial and accounting officer) |
39